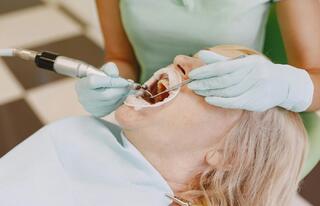
Everyone dreams of a healthy smile and strong teeth, but sometimes faces various problems: from tooth sensitivity to caries. Fluoridation of teeth is one of the most effective and accessible methods of prevention.
This article will reveal all aspects of tooth fluoridation: from its necessity and benefits to techniques and potential risks. We will detail how fluoride helps in the fight against caries, strengthens tooth enamel, and reduces tooth sensitivity. We will also address important questions: is fluoridation necessary for everyone, how often should it be done, and is it safe?
Fluoridation of Teeth - What It Is
This is a process of enriching the tooth enamel with fluoride-containing preparations to restore its composition. The procedure is affordable, painless, and suitable for most patients. It's an effective method for preventing and treating early-stage caries.
In dental clinics, varnishes and gels with fluorides are used. They are applied either once or as a course of treatment. As prescribed by a dentist, patients can use fluoride toothpaste or gel at home, applying them according to instructions 1-2 times a week.

Why the Procedure Is Needed
Fluoride is essential for teeth. Its deficiency accelerates demineralization and the development of caries. Fluoridation saturates the enamel with fluoride ions, restoring its ability to resist the acidic environment in the mouth. Fluoride compounds form a protective layer on the enamel, protecting the teeth from acids produced by pathogenic bacteria, and enriching them with fluoride and calcium ions.
Indications and Contraindications for Fluoridation
Fluoridation of enamel is used for:
- Prevention and treatment of early stages of caries;
- Enhancing the effect of professional dental cleaning;
- Reducing enamel sensitivity, especially in the neck area of the teeth;
- Restoring the mineral composition of enamel after whitening or orthodontic treatments.
The main contraindication is fluorosis. In such cases, remineralization without fluoride is performed.
Childhood is not a contraindication, but requires careful selection of products.
Caution is advised for patients with diabetes and allergies to components of the product.
Types of Enamel Fluoridation
1. Simple Fluoridation
Two types of fluoride-containing compositions are used:
- Fluoride gels, applied in silicone caps. They ensure good penetration into hard-to-reach areas. Several treatments are required.
- Fluoride varnishes, including single-component and multi-component with calcium and phosphates for enhanced remineralization.
The choice of preparation depends on the patient's condition. Single-component varnishes are usually suitable, but multi-component compositions are better for dry mouth or superficial caries.
2. Deep Fluoridation
Involves the application of remineralizing preparations containing fluoride, copper, magnesium, and calcium. The procedure is carried out in two steps:
- Cleaning the teeth from plaque and tartar, applying fluoride liquid for 1 minute. Removing liquid residues, drying the enamel, applying a suspension with calcium hydroxide.
A repeat session is recommended after 6 months.
Why is Deep Fluoridation Better?
Unlike the standard method, deep fluoridation seals micro-cracks in the enamel by applying remineralizing preparations in layers. This creates a dense mineral layer on the teeth with calcium, magnesium, and copper fluorides. This method strengthens the enamel and is ideal for treating the early stages of caries.
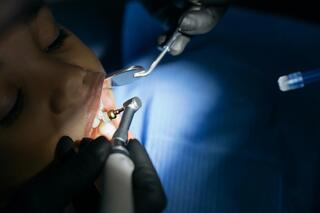
Steps of Fluoridation
-
Consultation and examination.
The dentist identifies any dental diseases and the need for additional treatment. -
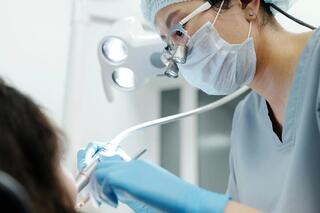
Professional dental cleaning.
First, dental plaque is removed using AirFlow or ClinPro methods, and tartar with ultrasound. Then, the teeth are polished with dental pastes. -
Fluoridation.
The dentist applies fluoride varnish, uses gel in caps, or performs layered fluoridation. The procedure is repeated after 5-7 days if necessary.
The patient is recommended home mineralization products, such as gels in caps or therapeutic toothpastes.
Recommendations After the Procedure
- Not to eat or drink for one hour;
- To avoid staining, acidic, cold, and hot foods and drinks for 24 hours;
- To replace the toothbrush and maintain thorough oral hygiene;
- To use therapeutic pastes and gels as recommended by the dentist.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is tooth fluoridation?
Tooth fluoridation is a procedure where a fluoride-containing product is applied to the teeth to strengthen the enamel and prevent cavities.
Why is tooth fluoridation necessary?
Fluoridation helps to strengthen tooth enamel, reduces the risk of cavities, and can help decrease tooth sensitivity.
How does fluoridation affect sensitive teeth?
Fluoridation can help reduce tooth sensitivity by strengthening the enamel and sealing microscopic channels in the teeth.
Can it be done at home?
High-concentration fluoride treatments are only allowed in dental clinics. For home use, therapeutic toothpastes and fluoride gels in caps can be used. The fluoride concentration in these products usually does not exceed 1.5%. Use them only after consulting with a dentist.
Remember, excess fluoride in the body can lead to serious internal organ disorders.
How often should the procedure be repeated in the clinic?
For preventive purposes, clinical fluoridation and remineralization are recommended every 6-12 months. For patients with problematic enamel, the interval between procedures is reduced to 3 months.
Is fluoridation harmful?
The procedure is harmless for both adults and children, provided that the dentist follows the treatment protocol and considers the clinical situation. The choice of product takes into account the fluoride concentrations in drinking water.
When treating baby teeth, it's important to consider the permissible fluoride concentrations for children of different ages. For children over 3 years, the same compositions as for adults are used, taking into account the risk of swallowing the product. For toddlers under 2 years, fluoride varnishes with a lower concentration of fluorides are recommended.
Is it suitable for pregnant and breastfeeding women?
The procedure is not only not contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding but is also desirable. This is due to a deficiency of fluoride and necessary minerals in the body of a pregnant woman and the risk of tooth tissue destruction. Fluoridation for pregnant women is carried out with precautions, and products are used strictly as indicated.
Is fluoridation safe for children?
Yes, fluoridation is safe for children, but it's important to use products with an appropriate fluoride concentration.
Is fluoridation necessary if there are no cavities?
Yes, fluoridation can be used as a preventive measure to avoid the development of cavities.
Fluoridation or remineralization: which is better?
Remineralization is a broader procedure that includes fluoridation. It is carried out with products based on calcium and phosphates, with or without the addition of fluoride. Which of these procedures is better depends on the indications. For example, only remineralization is performed in the case of fluorosis. After an examination in the clinic, the dentist will suggest the best treatment option for you.