What Is Tooth Whitening?
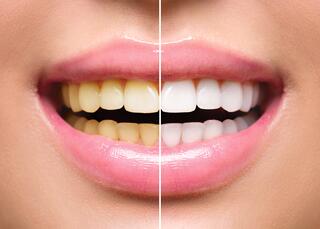
It's a series of professional techniques for brightening tooth enamel. It enhances the look of even teeth that are naturally yellow. Whitening gives the smile radiance and luminosity.
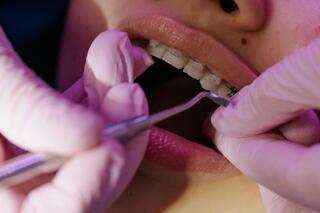
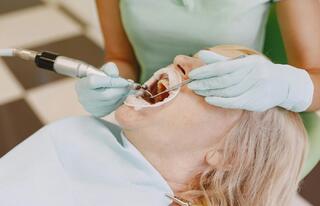
Before the whitening process, a dentist always carries out a detailed cleaning to eliminate plaque. After that, a bleaching agent is applied to the teeth. This gel deeply infiltrates the enamel, eradicating spots and embedded pigments.
For example, in dental offices, dentists might select a whitening technique based on the degree of enamel darkening. They assess the health of the mouth before settling on a whitening strategy – Zoom 4, Opalescence, Amazing White, KOR Whitening, among others.
Who Is Teeth Whitening For?
This service is ideal for individuals with:
- Yellow or brown discolorations.
- Tetracycline marks or fluorosis.
- Light marks on enamel following orthodontic braces.
- Enamel that has been darkened by smoking, age, or color-intense foods.
How Is Teeth Whitening Performed?
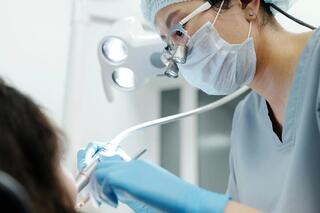
- The dental professional selects the right shade of enamel with the VITA scale.
- Protective eyewear is fitted to the patient, and the enamel is polished using a specific powder/paste.
- Lips are coated with a protective cream, and a napkin, a lip spreader, and cotton rolls are positioned in the mouth.
- A liquid barrier is applied to the gums to protect tissues from the bleaching agents.
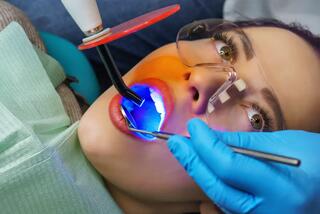
- The enamel is covered with a transparent gel that contains 35% hydrogen peroxide. This mixture is activated with a combined light accelerator lamp (LED + halogen). The process may include up to 3 cycles, each lasting 15-20 minutes.
- Afterwards, all protective barriers are removed from the enamel and oral cavity, and the teeth are treated with a protective solution to prevent sensitivity.
«Before lightening, it's essential to perform a professional teeth cleaning (Airflow/ultrasound) to eliminate both soft and hard deposits. This is necessary for the whitening agent to effectively reach the tooth tissues, ensuring the optimal outcome.»
Home vs. Professional Whitening: The Difference?
Whitening at home with professional-grade products can nearly match the effect of clinic-based whitening. Yet, whitening in a clinical setting offers several benefits:
- Professional Monitoring
The procedure in a dental practice is secure. A hygiene specialist protects the lips, gum margins, and mucous membranes to avoid chemical burns. They evenly distribute the whitening formula on the tooth's front surface, observing the change in enamel color and managing the duration of the whitening formula's application. - Immediate Results
Whitening performed at the clinic is completed within a single visit, lasting under an hour. You achieve a bright smile right after the treatment. - Optimal Effect
In a dental clinic, practitioners use a gel with a 35% hydrogen peroxide concentration (about five times higher than at-home whitening solutions), enabling a pronounced result in just 45 minutes – teeth become a minimum of 8 shades lighter. In contrast, at-home whitening results in a 2-4 shade improvement over two weeks. - Securing the Outcome
Following the whitening session, the dentist conducts a process to mineralize and fluoridate the enamel, enhancing its strength and preventing sensitivity. This method removes any immediate discomfort after the whitening, leaving you with a brilliant smile and zero discomfort.
«Even for home whitening, it's essential to initially visit a dental clinic for an oral clean-up to remove both hard and soft deposits from the teeth's surface.»
Professional Whitening Techniques
Depending on the individual case, contemporary clinics offer the following techniques for office whitening:
- Photo Whitening
This technique alters the enamel's shade using a special gel and halogen/UV/LED lights. The gel, activated by light, breaks down the pigmentation, brightening the enamel. - Traditional Chemical
With traditional chemical whitening, no catalytic devices (like a lamp or laser) are employed. The improvement in enamel shade is due to an oxidative reaction when a chemical gel is applied. Oxygen, serving as the active element, has a direct effect on the dentin. - Laser Whitening
Differing from photo whitening, here, a dental laser (either diode or neodymium) serves as the catalyst. The enamel is coated with a gel based on hydrogen peroxide, then exposed to a laser beam. As a result, oxygen is released from the gel, penetrating the teeth and dismantling the pigments. - Intracanal Whitening
Intracanal (endodontic) whitening is recommended for reviving the shade of darkened, depulped teeth. The procedure is performed from the pulp chamber side, filling the crown with a whitening formula (35% hydrogen peroxide/carbamide) and temporarily sealing it.
The gel inside the tooth decomposes, releasing active oxygen, leading to the whitening effect. The shade shift occurs gradually, so, unlike other methods, endodontic whitening requires multiple sessions (up to three per visit) with the agent being frequently refreshed. Upon achieving the targeted shade, a permanent seal is applied by the dental professional.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do teeth change color?
The shade of enamel can change for various reasons. The most common factors include poor oral hygiene, delayed dental treatment, smoking, excessive consumption of staining foods or certain medications.
How can you whiten your teeth at home?
You can lighten your teeth by a few shades at home using various whitening toothpastes or strips, and gel trays with a low concentration of the gel. Before using any method, we recommend consulting with a dentist to avoid damaging your teeth.
How do you maintain the effect?
To preserve the whitening results, maintain good oral hygiene: brush your teeth twice a day, use dental floss daily, and visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings. Avoid foods and beverages that stain teeth, such as coffee, tea, red wine, and dark berries. Use a straw when consuming staining liquids and rinse your mouth with water afterward.
When should you not whiten your teeth?
The main contraindications to office whitening include pregnancy, lactation, being under 18 years old, cancer, intolerance to the components of the whitening composition, and untreated dental and gum diseases.
Is teeth whitening safe?
Yes, teeth whitening is generally safe when performed under the supervision of a dentist. The key is to carefully follow the product's instructions and the dentist's recommendations. Excessive or incorrect use of whitening agents can lead to tooth sensitivity or gum irritation.
How long does the whitening effect last?
The longevity of teeth whitening results depends on the product used, dietary habits, and oral hygiene. Professional whitening can last from 6 months to 2 years. To extend the results, avoid staining foods and beverages and adhere strictly to oral hygiene rules.
Can teeth whitening damage enamel?
Most whitening products use hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, which temporarily open the pores in the enamel to remove stains but do not change the tooth structure in the long term. However, excessive use can lead to enamel erosion over time, so moderation is key.
Why do teeth become sensitive after whitening?
Sensitivity after whitening is common and usually temporary. The whitening process can temporarily dehydrate the teeth, making them more sensitive to temperature changes. This sensitivity should disappear within a few days after the procedure. Using toothpaste for sensitive teeth can help alleviate this discomfort.