Tooth Abscess
Have you noticed that your gum is swollen and red? Do you experience pain while chewing? These are signs of a serious condition – a tooth abscess. Learn why you should not ignore these symptoms and the dangers of not receiving treatment. We will also discuss the causes of an abscess, treatment methods, and answer common questions.
What is an Abscess? What Does It Look Like?
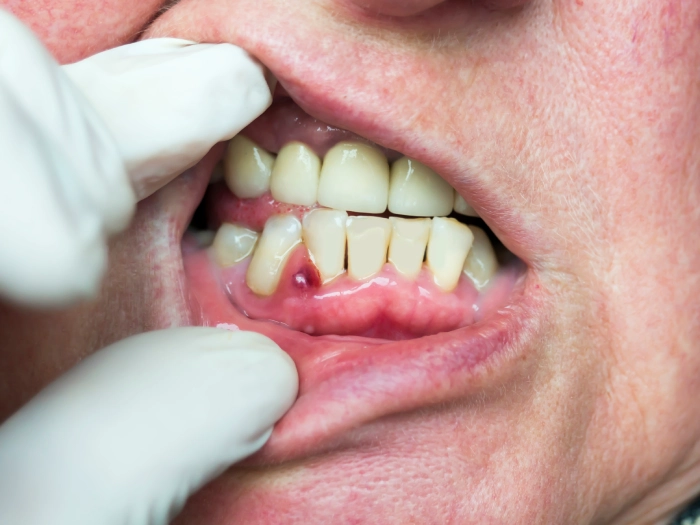
An abscess is an infectious and inflammatory condition that develops in the soft tissues near the tooth roots. The disease manifests as redness and swelling of the gums (forming a firm nodule) due to the accumulation of pus.
Why Does Pus Form?
When the number of pathogenic microorganisms in the mucosa increases, the blood supply to the periodontal tissues intensifies (causing the gums to turn red). Leukocytes, blood cells, move to the area of infection and destroy harmful microorganisms. Dead blood cells and bacteria form pus. Over time, it accumulates, leading to a purulent inflammation.
How to Recognize a Tooth Abscess?
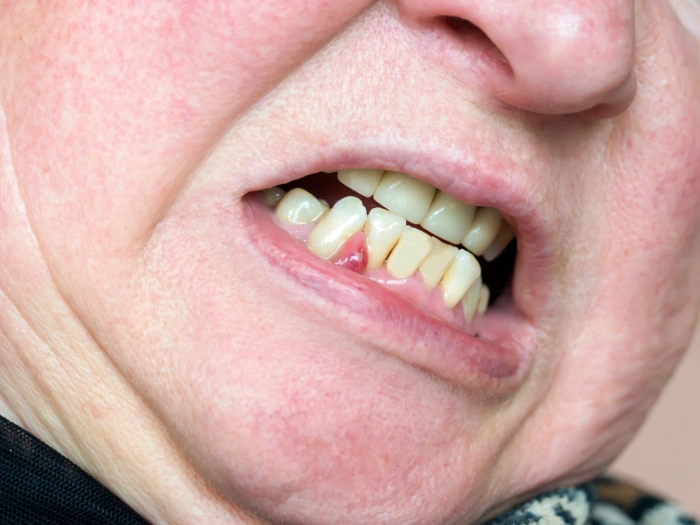
Symptoms of a tooth abscess include:
- Constant throbbing pain;
- Pain in the jaw and head;
- Discomfort from hot or cold food;
- Elevated body temperature;
- Sharp pain when pressing or chewing;
- Swelling, redness, and bleeding of the gums;
- Change in the color of the teeth, loosening of the tooth;
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth.
If you notice these symptoms, seek dental care immediately. Home treatment cannot completely eliminate an abscess, and remaining bacteria can lead to further spread of the infection.
How Does a Pustule Develop?
Symptoms of a tooth abscess include:
- An infection penetrates the soft tissue, forming an inflammatory focus with pus at the tooth or implant. A protective capsule forms around the abscess.
- At the site of inflammation, bacteria and lymph accumulate, forming a blister under the gum. The infection destroys bone tissue. The inflamed area can be painful.
- An abscess causes swelling and redness of the skin. The pus stretches the tissue, forming a boil on the mucous membrane. This can lead to symptoms of intoxication and impairments in chewing, swallowing, and breathing.
- Pus escapes through a fistula in the gum. Without treatment, the inflammation becomes chronic.
Causes
- Deep caries. Bacteria penetrate the pulp through destroyed tooth material.
- Injury. Scratches on the mucosa from brushing teeth or impacts can lead to infection.
- Periodontitis. Inflamed gums create conditions for the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Complications after tooth extraction. Failure to follow dental advice leads to infections in the socket.
- Incomplete root canal filling. Bacteria multiply in cavities, infecting the soft tissue.
- Pericoronitis. Infection under the mucosal cap when the wisdom tooth emerges.
What Do Dentists Say?
Why Do Abscesses Keep Occurring?
If the infection is not treated, bacteria can spread to other areas of the jaw, causing inflammation or new pus-filled areas.
Can an Abscess Develop After Tooth Extraction?
Yes, it's possible if the infection remains in the socket after extraction. However, this is rare as doctors treat the oral cavity with an antiseptic.
Can an Abscess Occur in a Healthy Person?
Yes. Bacteria can penetrate the soft tissue through a gum wound or due to traumatic tooth brushing.
Can Stress Cause an Abscess?
Yes, stress can reduce the body's ability to fight infection. In such cases, antibiotic treatment may be necessary.
Types of Abscesses
- Pericoronal. Pus forms in the gum over the emerging tooth, often over the wisdom tooth.
- Periapical. Inflammation in the root canals, pus accumulates at the root tip, forming a bump or fistula.
- Periodontal. The infection develops in the gum, between the bone and soft tissue, pus accumulates in a pocket, untreated it affects healthy tissues and bone.
- Gingival. Inflammation occurs on the surface of the gums, easy to treat, but can quickly spread, affecting the bone and adjacent teeth.
Stages of Pathology Development
The development process of an abscess:
- Initial gum inflammation;
- Formation of a small fluid-filled blister, 1-5 mm in diameter;
- Creation of a hollow pocket in the gum, accumulation of pus;
- Appearance of a fistula on the gum surface.
Without treatment, the abscess becomes chronic.
- Acute Stage. Symptoms are pronounced: severe pain, swelling of the pus-filled area, constant discomfort when eating and during temperature changes.
- Chronic Stage. The disease is less noticeable, pain is milder. Instead of a pus-filled area, a fistula forms. The infection remains, and the abscess can return.
What Happens If Not Treated in Time?
- Sinusitis. The infection penetrates the mucous membrane of the nasal sinuses, causing inflammation.
- Meningitis. An untreated abscess can reach the brain, which is dangerous and can lead to death.
- Sepsis. Blood poisoning due to infection. Symptoms include high fever, chills, mental disturbances, breathing difficulties, rapid heartbeat, and pain. Can be fatal.
- Phlebitis/Thrombophlebitis. Inflammation of veins and vessels due to purulent inflammation. Bacteria from the gum surface enter the blood, causing fever, pain, and weakness.
- Osteomyelitis. Bacteria from tooth roots spread to bone tissue, causing bone deformation.
Diagnosis
-
01Anamnesis and Complaint Collection
- The dentist inquires about the patient's dental diseases and abscess symptoms.
-
02Oral Cavity Examination
- The doctor checks the tooth for sensitivity to pressure, enamel color, cracks, oral hygiene, gum swelling, and mucosal redness.
-
03Laboratory Diagnostics
- In severe cases, blood tests are conducted to determine the infection and antibiotic sensitivity.
-
04Instrumental Examination
- Includes intraoral X-rays, panoramic jaw images, and CT scans to determine the source of infection and its spread.
How is an Abscess Treated?
Steps in treating an abscess:
Draining the Pus
1. For a gingival abscess, the doctor makes a small incision to remove the pus. The cavity is flushed with antiseptic or saline solution. A small rubber drain may be temporarily placed.
Surgical Intervention
2. Depending on the type of abscess:
- For a periodontal abscess, an incision is made to access the infection. Pus is removed through additional channels to prevent the spread of infection. Curettage of the periodontal pocket and treatment of periodontitis are performed.
- To treat a pericoronal abscess, tissue obstructing the tooth's eruption is removed.
3. Root canal treatment. For a periapical abscess, the infection is removed from the tooth. This involves opening, removing diseased pulp, draining, treating, and filling the canals. A crown may be placed if necessary. A follow-up examination is scheduled.
4. Tooth extraction. If the tooth cannot be saved, it is removed, and the pus-filled abscess is drained.
Conservative Treatment
1. Inflammation
To combat the infection, medications with antimicrobial and, if possible, pain-relieving effects are used. The goal is to eliminate harmful microorganisms, clean the wound, and promote its healing.
2. Wound Process
The wound is covered with healthy granulation tissue, which bleeds easily. In case of complications, the tissue is covered with a coating that slows down healing. In this situation, antibacterial ointments are applied.
3. Scar Formation
It is recommended to treat the mucous membrane around the wound to prevent reinfection.
What to Rinse With?
For local treatment of abscesses, antiseptic solutions are used. For rinsing the pus-filled cavity, aqueous solutions of chlorhexidine (0.02-0.05%), miramistin (0.01%), or dioxidine (0.1-1%) are suitable. A 3% hydrogen peroxide solution is recommended for pus discharge from the wound.
What to Apply?
Water-soluble ointments with antibacterial agents are used. Typically, the ointment is applied to the wound once a day. Commonly used antiseptic gels include Holisal and Parodontocid. For faster healing, ointments with regenerative substances like polyvinoks are prescribed.
How to Relieve Pain?
Ibuprofen helps alleviate discomfort while the gum heals. Medications like diclofenac, nurofen, and analgin relieve pain but do not treat the infection.
Are Antibiotics Necessary?
Antibiotics are prescribed if the infection spreads to the root area, other teeth, or the jaw, as well as in cases of weakened immune systems. Effective antibiotics for dental abscesses include amoxicillin, azithromycin, and metronidazole. The course of antibiotics usually lasts 7-10 days. After surgery, the doctor prescribes antibacterial therapy, including anti-inflammatory drugs and antiseptic rinses.
Treating an Abscess at Home
Home treatment cannot completely cure an abscess. Incorrect treatment can lead to complications. At home, one can only alleviate pain or clean pus if the pimple has burst.
Can You Open a Gum Abscess Yourself?
No, do not attempt to remove an abscess yourself. Consult a dentist! For severe pain, the doctor may recommend a pain reliever and methods for natural drainage of pus.
Does Salt Water Help with a Tooth Abscess?
Warm salt water only helps if the abscess has already burst. The salt solution cleanses the pus and stimulates drainage until you can visit the doctor. Dissolve a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth for 2 minutes.
How to Soothe the Gums?
Rinsing the mouth with chamomile or oak bark decoction can help with severe throbbing pain.
Can You Apply Heat or Cold to a Tooth Abscess?
Do not use heat for gum pain to avoid severe swelling. You can apply ice through a towel for a short time. Cold constricts blood vessels, reducing pain and swelling.
What Foods Can Be Eaten After Treating an Abscess?
Hard food can cause pain in the mouth. Switch to soft foods such as milkshakes, bananas, puree, yogurt, cereal with milk, an omelet or a soft pudding. It's important to maintain moisture in the mouth.
What to Do Before Visiting the Dentist?
Never attempt to open an abscess yourself. This can lead to a new infection in the open wound. See a doctor as soon as possible so they can clean the inflamed area and prescribe an antibiotic.
If it's not possible to visit a dentist immediately, you can alleviate symptoms at home. Do not use hot compresses and rinses, as they can worsen the inflammation.
- Use baths made from salt and baking soda solutions to disinfect, reduce inflammation, and draw out pus.
- Use chamomile or marigold decoctions for their antibacterial and soothing properties.
- A cleaned aloe leaf helps to draw pus from the gums.
Prevention
| To Do | Not to Do |
|---|---|
| Eat soft foods during periods of abscess formation. | Refrain from smoking |
| Change your toothbrush every 1-3 months. | Avoid consuming sweets, very hot or cold drinks, and foods. |
| Clean the spaces between your teeth with dental floss after every meal. | Do not rinse your mouth with antibacterial agents immediately after brushing your teeth. |
| Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft toothbrush. After brushing, spit out the toothpaste, do not rinse your mouth. | |
| Regularly visit the dentist for check-ups. |
Questions and Answers
Is a Gum Abscess Contagious?
NO. An abscess cannot be transmitted from one person to another.
Gum Abscess in Children?
Often, the cause of an abscess in children is tooth decay. Initially unnoticed, bacteria can enter the tooth. The infection in the soft and bone tissues forms a pus-filled sac. The child may notice a small, red swelling.
Associated symptoms of an abscess in a child include high fever, restlessness, and a reluctance to eat. If you detect a dental abscess in a child, urgently visit a dentist to prevent complications from the early stage of the disease.
Why Doesn't an Antibiotic Help with an Abscess?
- Antibiotic therapy was conducted without medical supervision, or the infection source was not eliminated.
- The cause is not bacterial. Antibiotics won't help if the abscess is caused by a virus or fungus.
- Incorrect choice of medication, when the pathogen is resistant to the drug, or the maximum concentration in the inflammation site is not achieved. This can happen during treatment, requiring a doctor's adjustment of the antibiotic therapy.
- Self-reduction of therapeutic doses, violation of dilution instructions, or administration technique.
Misuse of antibiotics leads to poorer treatment outcomes. To avoid complications, take antibiotics as prescribed by your doctor!
What Happens if You Swallow Pus?
Nothing serious! If pus drainage is incomplete, the infection may be released during sleep. This is normal, so the doctor prescribes antiseptic rinses.
Does the Gum Heal After an Abscess?
Most abscesses heal quickly after drainage and treatment of the infection source. Swelling on the gum remains for the first 2-3 days. The doctor will give recommendations to accelerate tissue growth for complete healing of the gum.
Who is Prone to Abscesses?
Patients with a weakened immune system, HIV, or after chemotherapy. Abscesses are also more common in diabetes or staphylococcus.
Risk groups include those taking steroids, antidepressants (which cause dry mouth), and immunosuppressants. Such patients should have a dental check-up at least once a year.
How Painful is Opening an Abscess?
The doctor performs the treatment under local anesthesia, so there will be no pain. During the opening and drainage of pus, the patient may feel slight pressure in the gum.
How to Sleep with an Oral Abscess?
Elevate your head to prevent blood from pooling and intensifying tooth pain. You can use several pillows or a cool compress.