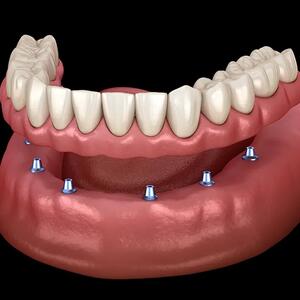
What is Dental Implantation?
Are you suffering from tooth loss and looking for a solution? At Dental Portal, we unveil everything about dental implants! Discover the various methods and types of implants that can restore your smile and confidence. Read our article to get the answers to your questions. Your first step towards a perfect smile begins here!
What is it?

Implantation is a reliable method to restore all teeth. In this procedure, a titanium rod with a thread is inserted into the jaw. Then, an abutment and a crown made of metal-ceramic or zirconium are attached. This method allows:
- Restoring all teeth.
- Stopping the atrophy of the alveolar process.
- Fully restoring the chewing function.
- Correcting the bite.
Implantation Methods
Immediate Implantation:
Insertion of the artificial root immediately after tooth extraction.
- No need for bone grafting and gum incision.
- Possibility to fit a temporary crown on the day of surgery.
Classic Implantation:
Two-stage implantation.
- Reliable and clinically proven technology.
- Bone grafting required for insufficient alveolar process volume.
All-on-4:
Restoration of the entire set of teeth in one day in cases of complete edentulism.
- No need for bone grafting even in cases of bone atrophy.
- Suitable for progressive periodontitis.
All-on-6:
An advanced version of the All-on-4 protocol. A fixed prosthesis is attached to six titanium rods, two of which are placed on the sides. This ensures high initial stability.
- Suitable for complete tooth loss or when it's impossible to save remaining front/back teeth.
- Applicable for severe forms of periodontosis/periodontitis.
- Used when there's a significant reduction in the alveolar process.
Zygomatic Implantation
An innovative method for restoring teeth in the upper jaw. The procedure is performed without bone grafting, even with substantial bone loss. Long Nobel Zygoma or Zygomatic implants from Noris (up to 60 mm) are used.
Combines various implantation methods (immediate, traditional) and types of titanium rods (standard, basal, compression).
- Suitable if there are no teeth in the upper jaw or the remaining ones need to be removed.
- Not suitable for "All-on-4/All-on-6" protocols.
- Not recommended when increasing the height/thickness of the bone tissue is not possible.
Types of Implants
Endosteal:
- Universal titanium rods suitable for various implantation methods (immediate, single-stage, two-stage). Available in modular and solid designs.
Advantages:
- High success rate.
- Wide range for different cases.
- Easy to place.
Disadvantages:
- Often requires sinus lifting, bone grafting.
- Numerous restrictions.
Zygomatic:
Long pins inserted into the zygomatic bone. Characterized by no inflammation and resistance to atrophy. Zygoma rods (Nobel Biocare) and Zygomatic (Noris Medical) are used for significant alveolar process loss.
Advantages:
- Possible to place in patients with diabetes, periodontitis.
- Excellent initial stability.
- Suitable even with severe bone loss.
- Used for immediate loading of the prosthesis.
Disadvantages:
- High cost.
- Requires high surgical expertise.
- Limited application (only upper jaw).
Basal:
Implantation into the dense bone layer – basal.
Advantages:
- High initial stability.
- Thin bone layer is not a problem.
- Placement in both jaws without gum incision.
Disadvantages:
- Traumatic method.
- Long rehabilitation period.
- Does not fully restore chewing function.
- Higher risk of rejection.
Mini Implants:
Often used as a temporary solution (for securing prostheses). Most are single-piece, up to 1 cm long.
Advantages:
- Minimal trauma.
- Affordable price.
- Placement without bone augmentation.
Disadvantages:
- Short lifespan (2-3 years).
- Special care requirements.
- Do not ensure stable construction.
Indications
- A damaged tooth that needs to be removed.
The immediate implantation method can be used. The tooth is removed, and an artificial root is immediately inserted. A temporary fixed prosthesis is placed after a few hours (if there are no restrictions) or within 3-7 days. - Missing a front tooth/molar.
Functionality and appearance of the dental row are usually restored with a single-stage implantation with immediate loading. A temporary crown is attached to the titanium rod right after placement. - Removal of 2-3 consecutive teeth.
The best solution is a bridge prosthesis on metal-ceramic or zirconium dioxide, supported by two implants. Alternatively, titanium rods can be placed where each tooth is missing. Depends on the clinical situation and other factors. - Complete tooth loss.
Full prosthetics are performed according to one of the protocols: Zygoma (only for the upper jaw), All-on-4/All-on-6, implantation with immediate loading. The method is chosen by the doctor after examination, questionnaire, analyses, and CT.
Contraindications
| Relative Contraindications | Absolute Contraindications |
|---|---|
| Viral infections. | HIV. |
| Pregnancy or breastfeeding. | Tuberculosis. |
| Presence of cysts, granulomas. | Drug addiction. |
| Dental issues such as tartar, caries. | Chronic alcohol consumption. |
| Reduction in the volume of the alveolar process. | Malignant tumors and autoimmune diseases. |
Stages of Implantation
Examination of the oral cavity and consultation (1 hour). The patient undergoes a blood test for laboratory studies. The doctor learns about the patient's chronic diseases, allergies to medications.
Diagnostic imaging (1-2 hours). CT and X-ray are performed. Panoramic images are carefully analyzed. Possible contraindications for the surgery are identified.
3D modeling. A key phase that allows for the precise selection of titanium rods and their placement at the correct angle.
Signing a contract that describes all stages up to the placement of the prosthesis.
Professional oral hygiene (2-4 hours). Removal of dental deposits and, if necessary, sanitation of the oral cavity.
Surgical phase (15-20 minutes per implant). Artificial roots are implanted into the jaw under anesthesia. A temporary prosthesis is placed after 3-4 hours or days in cases of immediate/single-stage implantation.
Regular check-ups and placement of the permanent prosthesis. Monthly dental visits are necessary during osseointegration for monitoring. After integration, the permanent construction is installed.
Questions and Answers
What are dental implants?
Dental implants are artificial titanium tooth roots that are placed into the jawbone to secure a tooth, bridge, or denture. They serve as a long-term solution for replacing missing teeth.
Who is a candidate for dental implants?
Ideal candidates are individuals over 18 years old who are missing one or more teeth, have sufficient jawbone mass, and good overall oral and general health. In cases of insufficient bone mass, a procedure such as bone grafting may be recommended.
Are dental implants painful?
The implantation procedure is generally painless as it is performed under local or general anesthesia. Some discomfort or pain may occur during the initial recovery period, but this can usually be managed with prescribed pain relievers.
What is the success rate of dental implants?
Dental implants have a high success rate, typically around 98%. Success depends on factors such as the implant material, the patient's overall health, and the skill of the dentist or oral surgeon.
How long do dental implants last?
With proper oral hygiene and care, dental implants can last a lifetime. The implant material (titanium or ceramic) is durable and resistant to decay, although the crown may need replacement every 10-15 years due to wear.
How much do dental implants cost and are they covered by insurance?
The cost varies depending on individual needs, the amount of bone tissue, and the region. Some insurance plans may cover part of the cost, but this depends on the specific case.